EMPLOYABILITY AND ENTREPRENEURIAL SKILLS
LEVEL 4
Employability and Entrepreneurial Skills
TASK 1 - INDIVIDUAL TASK
Question 1 (5 Marks)
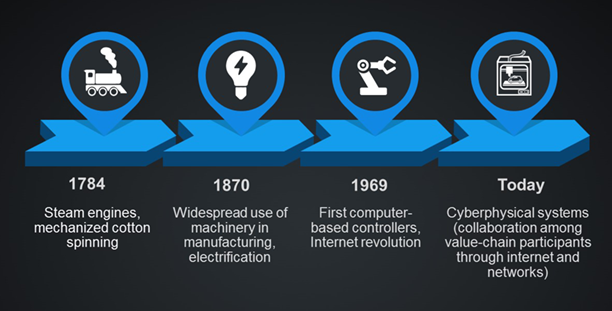
Keeping in mind the 4th Industrial Revolution, choose a job opportunity and describe at least three (3) different transversal skills that an employer would look for when choosing candidates to fill the post. (5 Marks)
Assessment Rubric:
- 1-2 Marks for description of job opportunity and how it is impacted by 4th Industrial Revolution, and
- 1 mark for each transversal skill including description of why it is relevant for the job opportunity (Max. 3 Marks)
Question 2 (7 Marks)
Reflect on any skills that you currently possess that might help you to find employment. Analyse what skills you need in order to make yourself more employable and stand out from the rest of the potential candidates for a job opportunity.
Assessment Rubric:
- 1 mark per skill that student currently possesses, including description of why it is relevant to job opportunity (Max 3 Marks)
- 1 mark for each skill that needs to be acquired (Max 2 Marks)
- 1 mark (per skill) for detail of how skill will be gained/improved (Max 2 Marks)

|
21st Centrury Skills - How Can You Prepare Students For The New Global Economy.pdf Size : 788.528 Kb Type : pdf |

|
21st Century Skills Handout.pdf Size : 379.173 Kb Type : pdf |

|
Employability Skills Required by the 21st Century.pdf Size : 2301.518 Kb Type : pdf |
Transversal Skills - UNESCO
https://unevoc.unesco.org/go.php?q=TVETipedia+Glossary+A-Z&id=577
Transversal skills are those typically considered as not specifically related to a particular job, task, academic discipline or area of knowledge but as skills that can be used in a wide variety of situations and work settings (IBE 2013). These skills are increasingly in high demand for learners to successfully adapt to changes and to lead meaningful and productive lives. Examples include:
• Critical and innovative thinking
• Inter-personal skills (e.g. presentation and communication skills, organizational skills, teamwork, etc.)
• Intra-personal skills (e.g. self-discipline, enthusiasm, perseverance, self-motivation, etc.)
• Global citizenship (e.g. tolerance, openness, respect for diversity, intercultural understanding, etc.)
• Media and information literacy such as the ability to locate and access information, as well as to analyse and
evaluate media content (UNESCO 2014c)
Source: UNESCO (Bangkok) 2014, Asia Pacific

|
EntrepIntro.pptx Size : 1898.742 Kb Type : pptx |


|
The Most Successful Startups Have Hands-On Founders.pdf Size : 207.06 Kb Type : pdf |
TASK 2 - GROUP TASK
Q3: Idea Generation Techniques
Question 3 (10 Marks)
As a Team, you are required to come up with entrepreneurial ideas. Use an idea generation technique to come up with a number of (minimum three) business ideas. Your answer should include:
- An explanation of the process through which ideas were generated.
- A description of three Business ideas.
- The market sector relating to each business idea.
- Diagrams, table etc. that might help you explain better the idea generation process can be included in your answer.
- Max 6 Marks for explanation of the idea generation process. Refer to Marking scheme for details of the 6 marks.
- 1 Mark for each business idea described (Max 3 Marks)
- 1 mark for mentioning market sector of all business ideas (Max 1 Mark)
Idea Generation Techniques
- Brainstorming
- Mind-Map
- SCAMPER
- Delphi Method

Q4: Selecting the Best Idea
Question 4 - (6 Marks)
From the pool of ideas identified in Question 3, choose an idea that fits best for your team in order to take the idea a step further and write up a proposal. Write down the chosen idea and include:
EITHER
- A matrix scoring system showing three (3) ideas and minimum three (3) factors. Include a description of your thought process
OR
- An Originality Pane matrix
OR
Any type of analysis to show how evaluation of the ideas was done, in order to choose the idea you want to take forward (e.g. SCAMPER or Delphi Method - see videos above)
Assessment Rubric:
- If a matrix scoring system, originality pane etc. is used, allocate between 0 and 3 marks for the table/diagram etc., based on proper use of tool. [For the matrix scoring system, 3 ideas with 3 factors are required.]
- and
- Allocate between 0 and 3 marks for the description of the thought process, using the marking scheme (Max 6 Marks)
Example of a Matrix Scoring system - The Product Demand Matrix
Business Evaluation matrix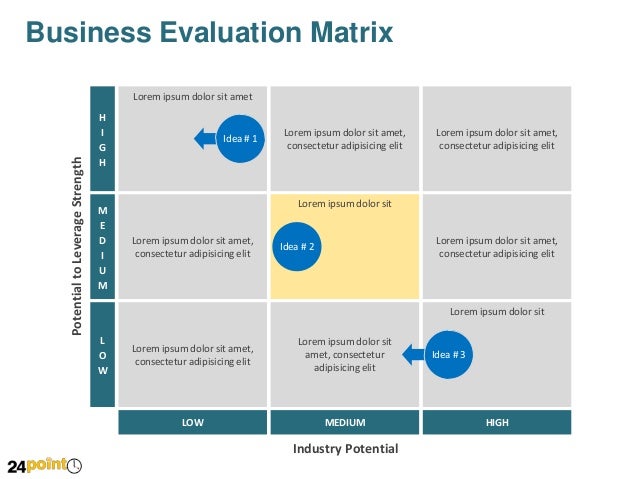

The 'Originality Pane' matrix
Example of a Business Evaluation Matrix System (3x3)
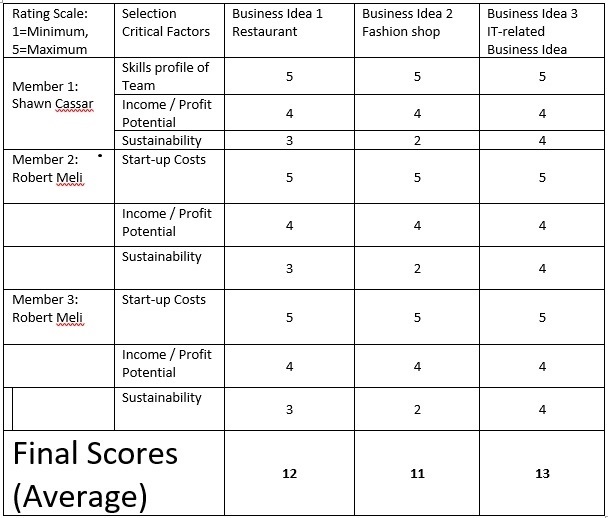

|
The-Idea-Evaluation-Matrix.pdf Size : 218.989 Kb Type : pdf |
Q5: SWOT Analysis of Chosen Idea
Question 5 (8 Marks)
Analyse your internal and external environment and list Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats (SWOT) related to your chosen idea.
Assessment Rubric:
- 2 Marks for each of S, W, O and T (Max 8 Marks) each using marking scheme.
- For Maximum 8 marks - Four (4) or more valid points are presented/listed in each 'quadrant'.
A SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats) analysis looks at internal and external factors that can affect your business.
Internal factors are your strengths and weaknesses.
External factors are the threats and opportunities.
SWOT is an acronym used to describe the particular Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats that are strategic factors for a specific company. A SWOT should represent an organization’s core competencies while also identifying opportunities it cannot currently use to its advantage due to a gap in resources.
The SWOT analysis framework has gained widespread acceptance because of its simplicity and power in developing strategy. Just like any planning tool, a SWOT analysis is only as good as the information that makes it up. Research and accurate data is vital to identify key issues in an organization’s environment.
For even more of a deep dive on the subject, you can watch our video on How to Perform a SWOT Analysis.
Assess your market:
- What is happening externally and internally that will affect our company?
- Who are our customers?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of each competitor? (Think Competitive Advantage)
- What are the driving forces behind sales trends?
- What are important and potentially important markets?
- What is happening in the world that might affect our company?
- What does it take to be successful in this market? (List the strengths all companies need to compete successfully in this market.)
Assess your company:
- What do we do best?
- What are our company resources – assets, intellectual property, and people?
- What are our company capabilities (functions)?
Assess your competition:
- How are we different from the competition?
- What are the general market conditions of our business?
- What needs are there for our products and services?
- What are the customer-market-technology opportunities?
- What are the customer’s problems and complaints with the current products and services in the industry?
- What “If only….” statements does a customer make?
Opportunity is an area of “need” in which a company can perform profitably.






Q6 (Part a): Primary Research (11 Marks)
Question 6a and 6b (11 Marks)
Part A
Use primary research to identify your target market. This could be in the form of questionnaires (minimum 50) or interviews (minimum 6) etc. One blank copy of the questionnaire or any other material gathered, together with a summary of results (eg. through charts, transcripts, etc.) obtained should be included in the Appendices.
Part B
Design a fan-fold brochure in order to promote your product/service. Keep in mind the information gathered from the primary research when creating your brochure. Make sure that the design is relevant to your product/service and appealing to your target audience. Necessary permissions need to be obtained for pictures that will be included in your brochure. To present the brochure as part of the assignment document, you are advised to use two pages in landscape layout each split into three (3) sections. The structure could be similar to the diagrams shown in Figure 1 and Figure 2 of the assignment brief.
- Business idea is described clearly and in detail through a Problem-Solution-Benefits format. (4 Marks).
- Description shows a clear identification of the target market, which corroborates with primary research results. Primary research was conducted with a range of possible target customers. Minimum of 50 questionnaire results or 6 interviews were used. (3 Marks).
- Design of brochure is valid, includes an element of pleasant aesthetics that is designed to attract the target audience's attention. Brochure includes all necessary sections indicated in assignment brief (About the business/company, contact details, front page [name-logo-tagline], problem-solution-benefits, target market, pricing). (4 Marks).
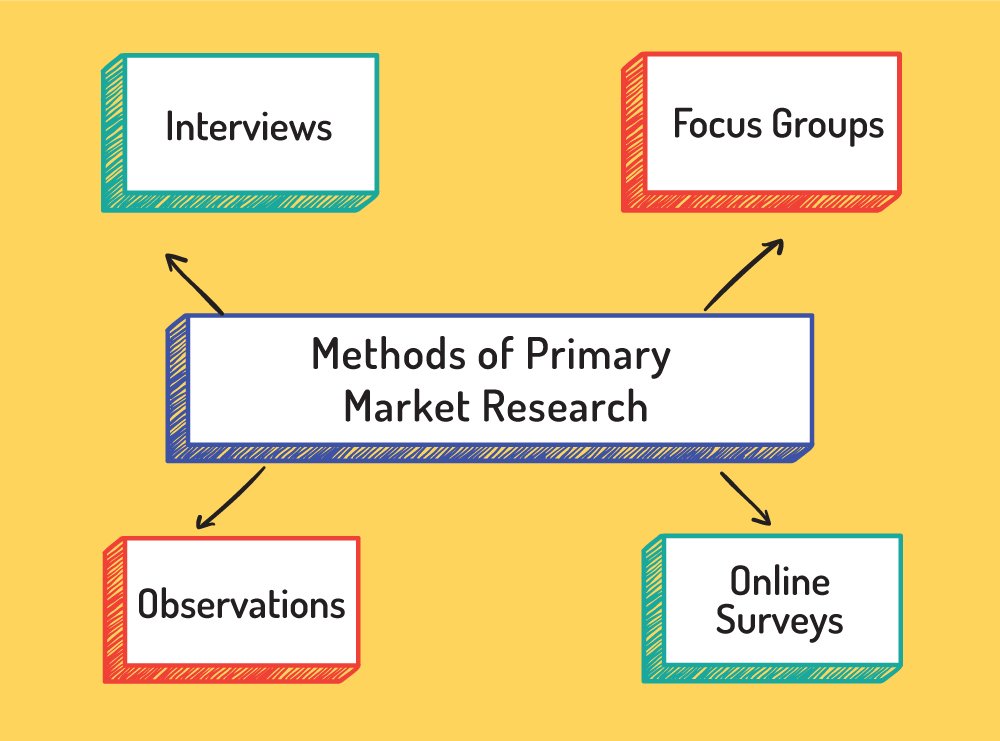
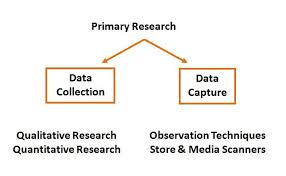
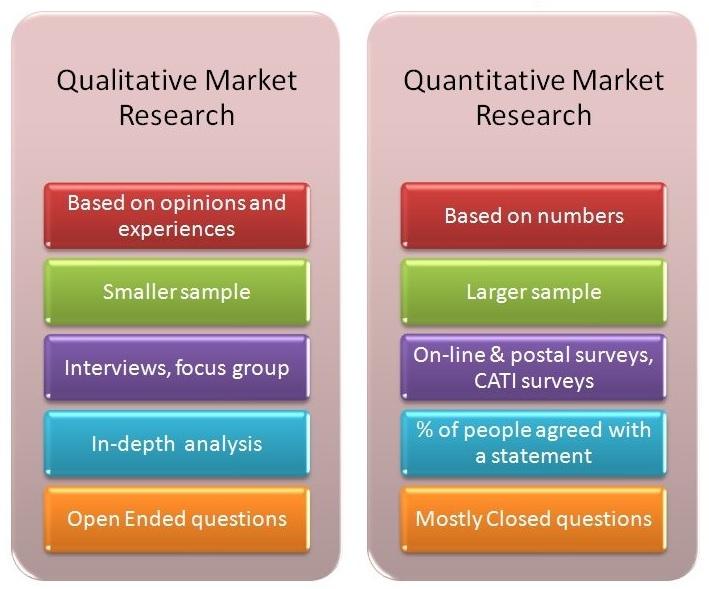
Finance
- Fixed and Variable Costs
- Positive and Negative Cash Flow
- Sources of Funding

|
Financial Aspects of Marketing Management.ppt Size : 375.5 Kb Type : ppt |
Recognize the broad operational, legal structures and financial aspects that affect a new enterprise.
Operational Structures
- Type of business structure and the reasons behind choosing the type of structure.

|
Business Structures.ppt Size : 585 Kb Type : ppt |
Customer Benefits and Unique Selling Propositions (USPs)

|
Unique Selling Proposition.ppt Size : 1070.5 Kb Type : ppt |
Target Customers and Purchasing Behaviour

|
Identifying Target Audience.ppt Size : 3610.5 Kb Type : ppt |
SWOT Analysis
Conduct different types of market research leading to a Marketing Plan.
- SWOT analysis.

|
SWOT-Analysis.ppsx Size : 975.504 Kb Type : ppsx |
Competitor Analysis
- Competitor Research and Analysis.

|
Competitor Analysis.ppt Size : 3828 Kb Type : ppt |
Market Research - Primary Research
Conduct different types of market research leading to a Marketing Plan.
- Primary research: Designing questionnaires and field research in the marketplace.

|
Pre-Survey - Market Research.docx Size : 64.807 Kb Type : docx |

|
Market Research.ppt Size : 2618.5 Kb Type : ppt |

|
Primary Research.pptx Size : 470.807 Kb Type : pptx |
Market Research - Market Analysis
Conduct different types of market research leading to a Marketing Plan.
This section is about what one can supply and sell, as opposed to selling what one can make or provide. Market research is therefore critical for this section. This shall be introduced as follows:
Market analysis (secondary research).

|
Market Research for the Green Venture.pptx Size : 1141.683 Kb Type : pptx |
Key Trends In The Economy
Understanding key trends and explore opportunities in the economy.
- People living longer and smaller families; implications for health services and residential care.

|
L4 - LO1 - 05. People living longer smaller families Implications for health.pptx Size : 4419.075 Kb Type : pptx |
Session 5: Learning Outcome 1 (Week starting Monday 23rd October 2017)
Understanding key trends and explore opportunities in the economy.
- The increased participation of women in the labor market.

|
L4 - LO1 - 04. Changing Families and Female Participation in the Labour Market.pptx Size : 3101.922 Kb Type : pptx |
Understanding Key Trends In The Economy
Understanding key trends and explore opportunities in the economy.
- Financial Services in Malta
- iGaming business sector (SIGMA, 2016)
- Starting a new business in Malta.
Understanding Key Trends and Opportunities In The Economy
Understanding key trends and explore opportunities in the economy.
Changes in growth value asset (e.g. between 1980 and 2014 Industry saw the following changes: Agriculture from 4% to 2%; Industry from 38% to 17%; Services from 59% to 81%. Targeted
strategy to attract foreign direct investment opened up new service sectors.Higher value added activities generated by the financial services sector, specialized forms of tourism – like language schools and dive centers – maritime activity, professional services,
back-office administration (security, office administrative and support services), information technology and gaming, financial services, legal and accounting services, gambling & betting and private education, the arts, entertainment and recreation sector.- Where does the Maltese economy stand today?
- What is contributing to the growth of the Maltese economy?
- What is the strategic position of Malta?
- Diversification of our economy.
Understanding Key Trends In The Economy
Understanding key trends and explore opportunities in the economy.
- The Services sector.
- From Labor-intensive to High-end technology manufacturing.

|
L4 - 02. Services Sector (J. Cilia).ppt Size : 2883.5 Kb Type : ppt |
Level 4 -Entrepreneurship
3 Hours a week - Semester 1
Overall Teaching Aims
The central learning element in this study unit is the identification and development of a business idea.
More specifically, the unit focuses on transforming the learners’ sense of creativity into the design and development of a business proposal.